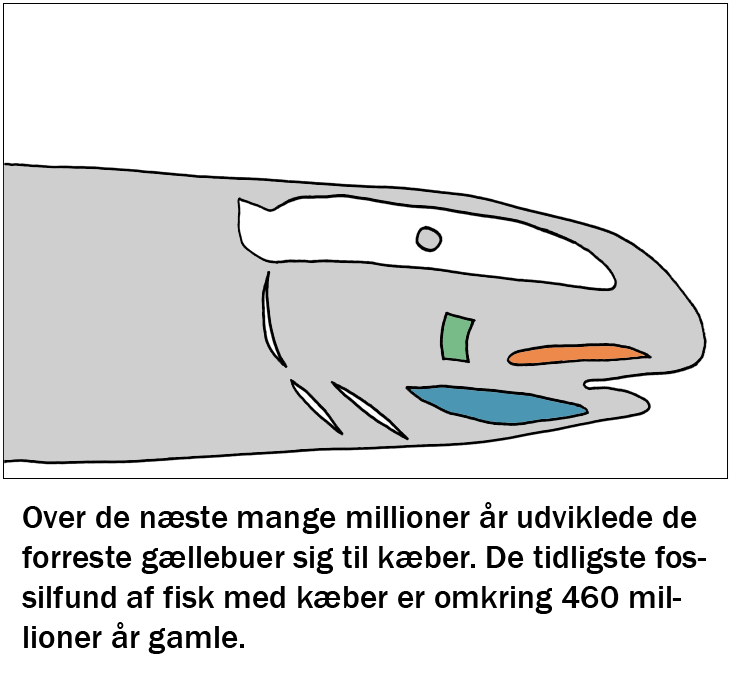
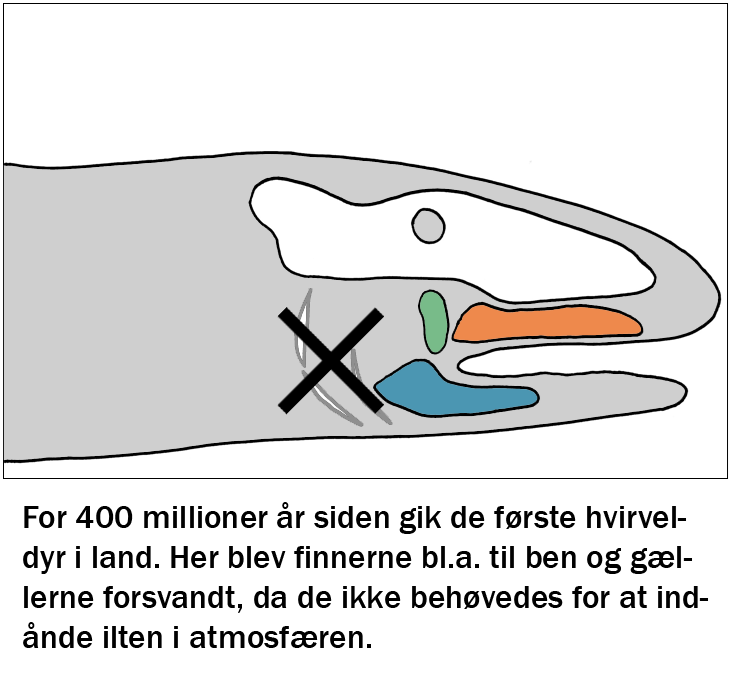
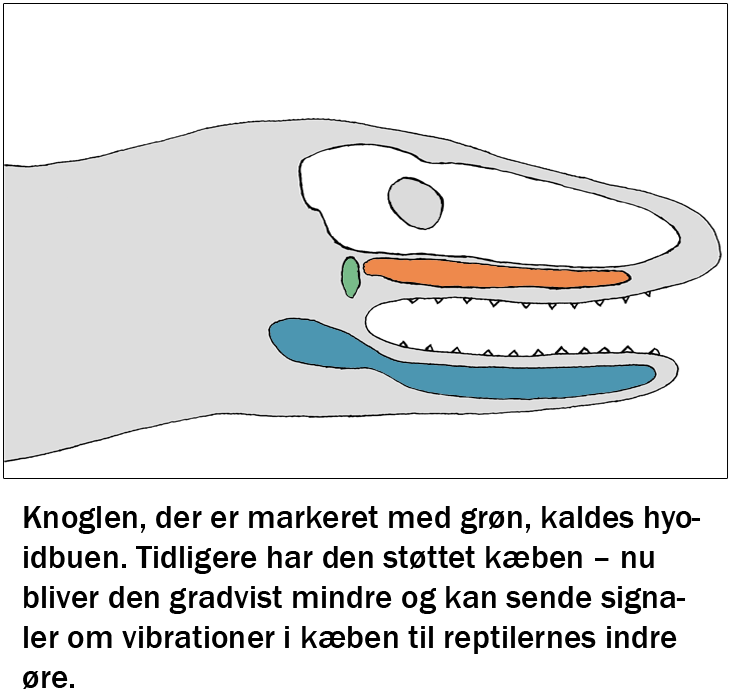
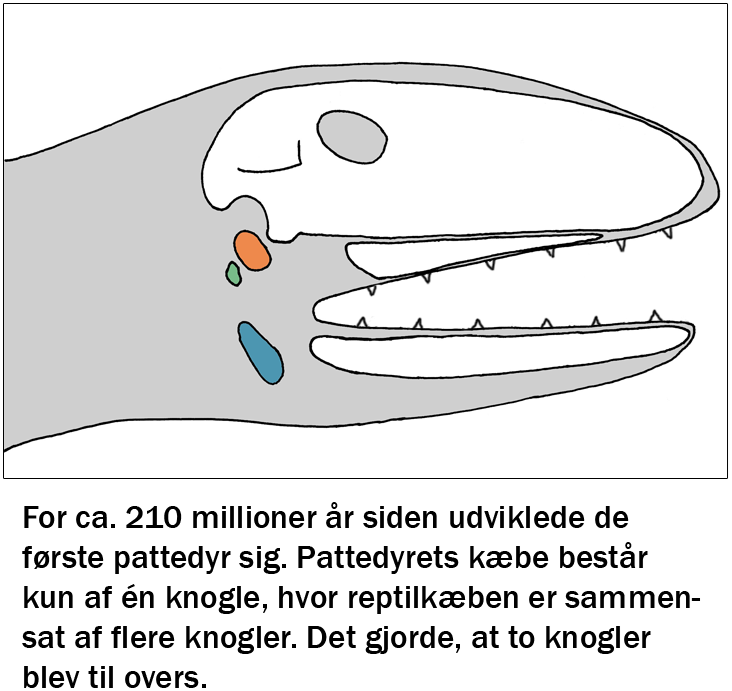
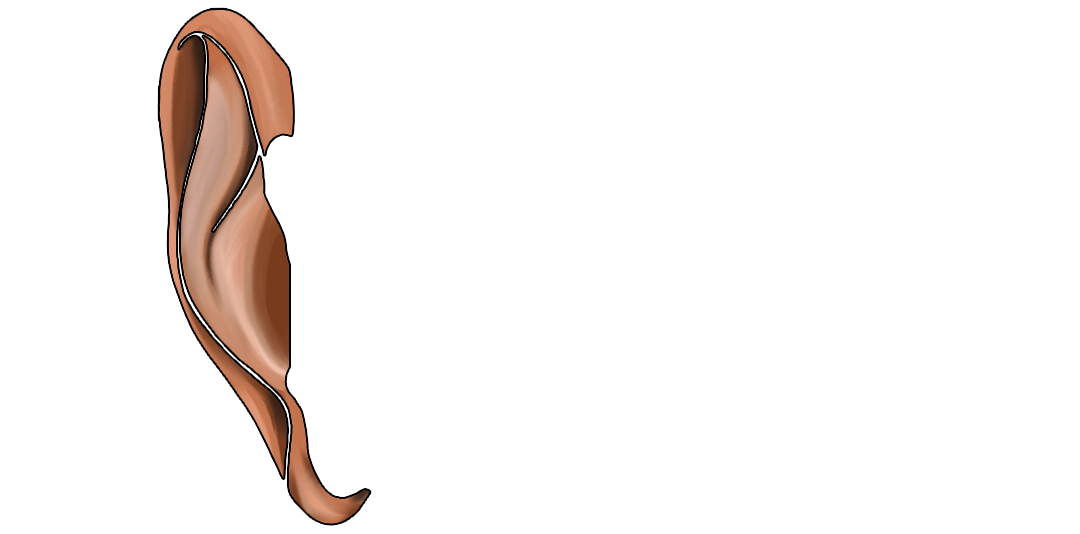Welcome to the education page. Here you can find educational programs for free use by teachers from Struer Statsgymnasium in the subjects physics, biology and music / psychology. All learning material has been tested and adjusted. Enjoy.
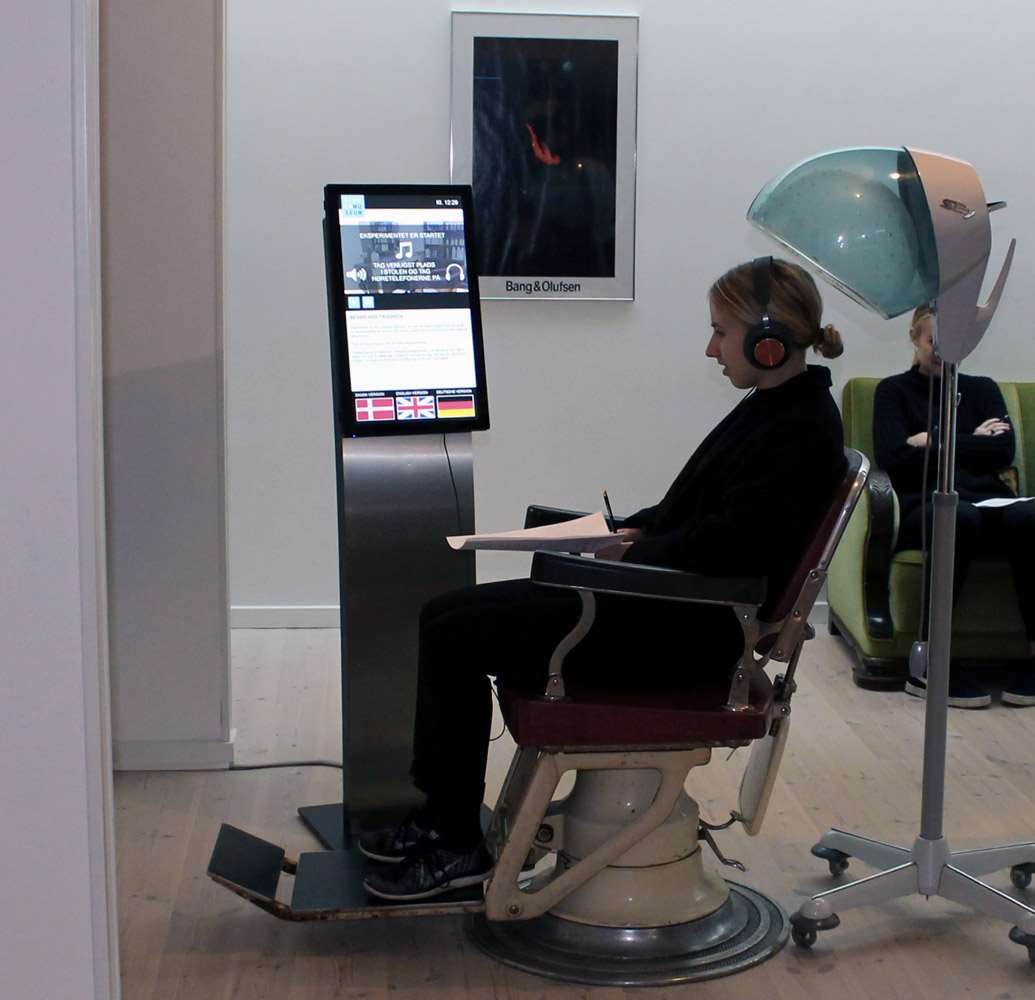
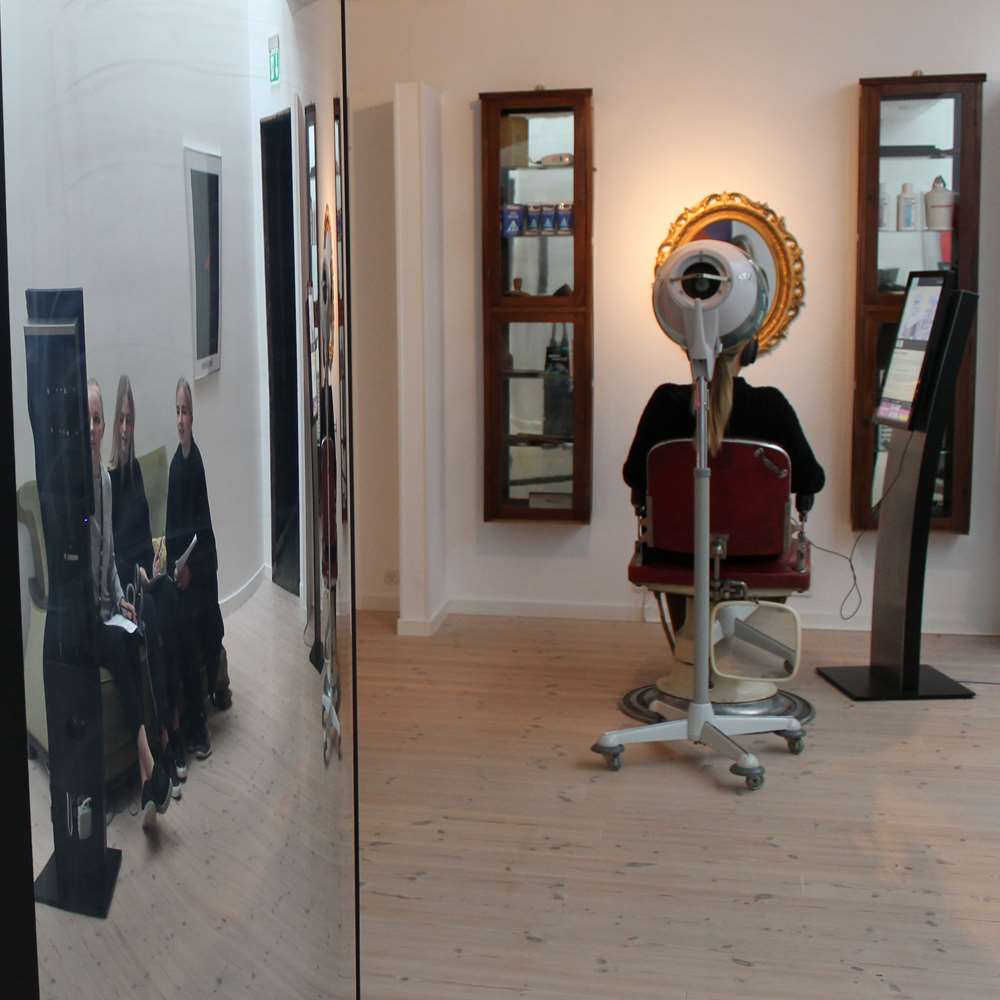


Teaching courses in music and psychology
The purpose of the course is to investigate the influence of music on pupils' ability to solve cognitive-based tasks - including the students emotional experience of it and knowledge of its structure has an impact on the outcome. Students thus gain knowledge about how their musical skills can be used as learning tools in other subjects. In psychology, the cognitive results can form the basis for inspiration for later experimental work, eg in psychology B / C on stx or Internal Assessment for 2nd year IB students.
Music, Brains, and Likes; Call - Overs & Oslash; Overview
Appendix 1 - Sound exhibition - Activities
Appendix 2 - Erik Christensen - Music is directly in the body



Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, velit tempor class reprehenderit cum commodo, felis eget, vel duis suspendisse at quis vivamus rhoncus. Ipsum quam posuere quis donec, ligula rutrum eu lobortis purus, elit iaculis felis magna, habitasse eget donec neque augue ante, egestas eleifend etiam diam eu. Pellentesque nam id erat urna donec at. Justo nam, tristique eros, sed lorem, mollis magna, in consequat pede. Nulla et ut condimentum pede tristique tincidunt, fames ultrices etiam congue nullam gravida, nunc justo ullamcorper proin vitae, libero ultricies massa, imperdiet a ornare.



Teaching courses in biology
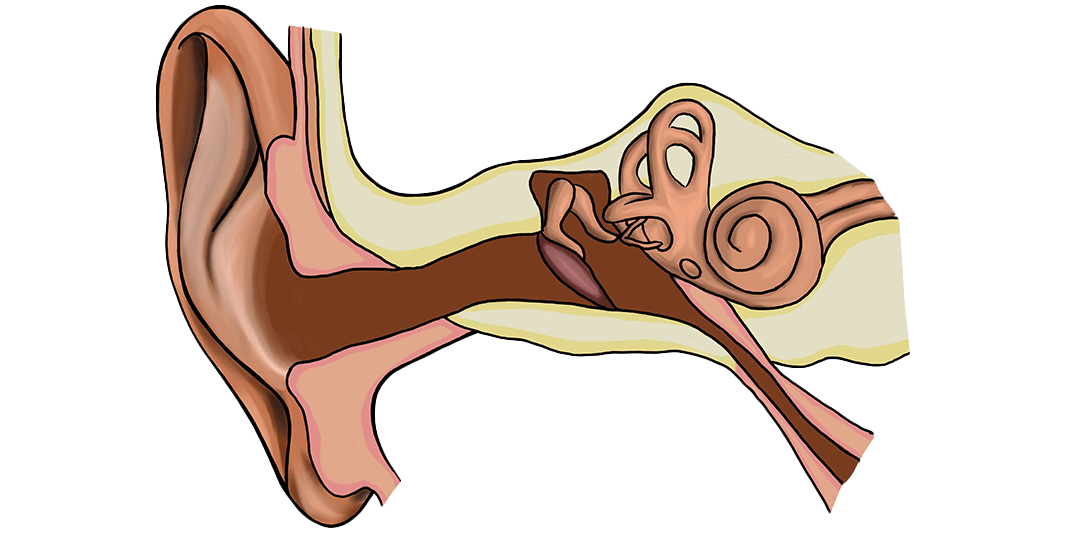
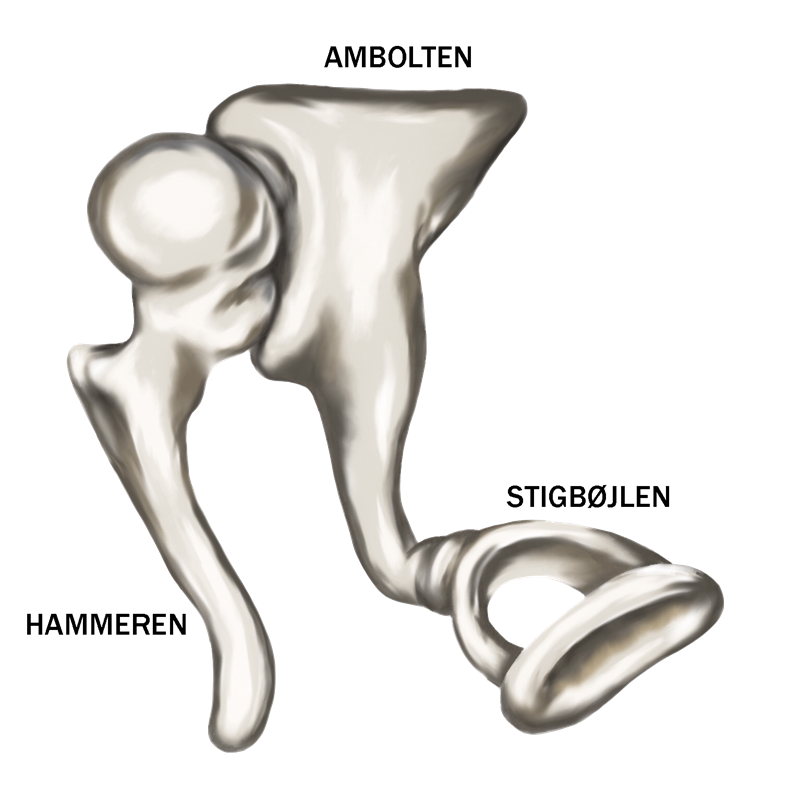
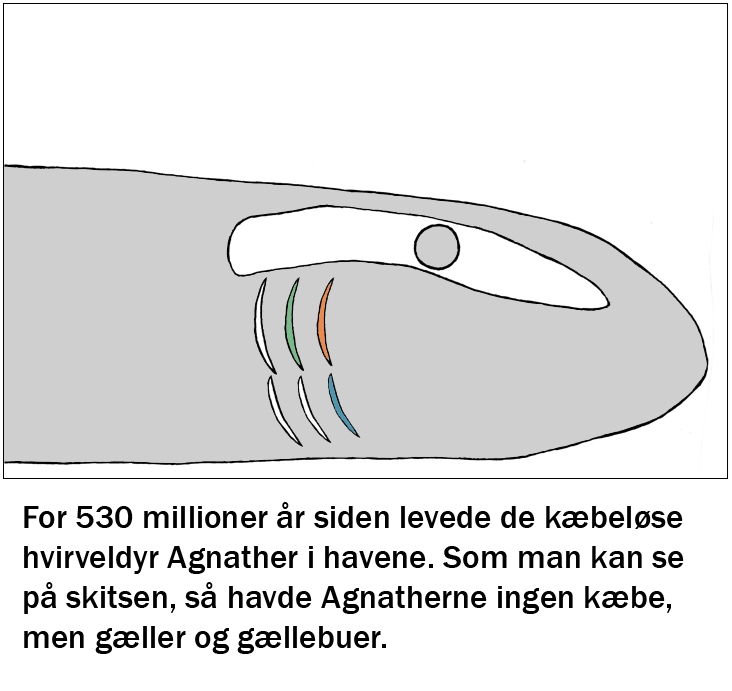
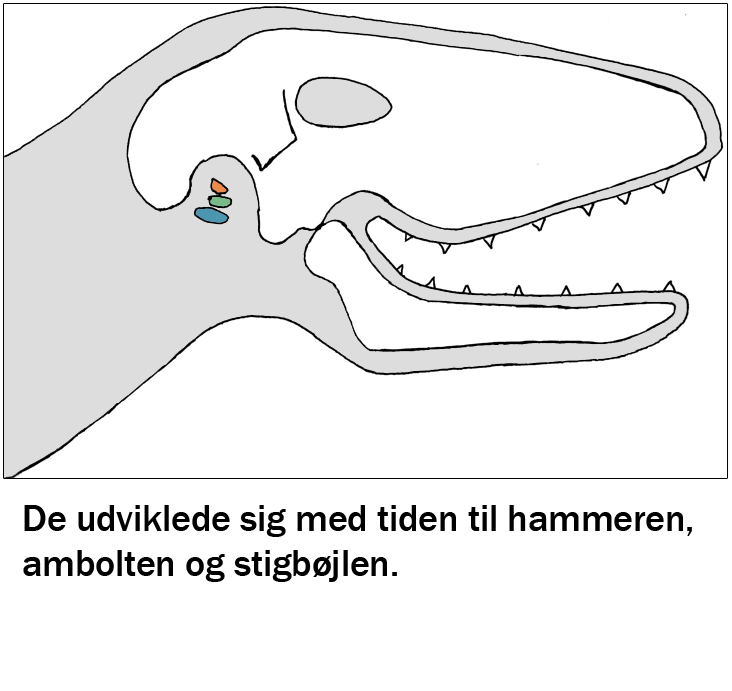
Focus in the process is the development, application and importance of sound, hearing and music in humans compared with whales and dolphins. The starting point is the team's experience in the audio universe, and the course develops from there to work with sound in several different levels and ways. The course is part of a larger coherent course of evolution, nerves and hormones. The "sound course" covers the anatomy of the ear and the impact of music on memory, learning and stress.



Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, velit tempor class reprehenderit cum commodo, felis eget, vel duis suspendisse at quis vivamus rhoncus. Ipsum quam posuere quis donec, ligula rutrum eu lobortis purus, elit iaculis felis magna, habitasse eget donec neque augue ante, egestas eleifend etiam diam eu. Pellentesque nam id erat urna donec at. Justo nam, tristique eros, sed lorem, mollis magna, in consequat pede. Nulla et ut condimentum pede tristique tincidunt, fames ultrices etiam congue nullam gravida, nunc justo ullamcorper proin vitae, libero ultricies massa, imperdiet a ornare.